If you happen to be viewing the article Introduction to the Definition of Measurement in Math? on the website Math Hello Kitty, there are a couple of convenient ways for you to navigate through the content. You have the option to simply scroll down and leisurely read each section at your own pace. Alternatively, if you’re in a rush or looking for specific information, you can swiftly click on the table of contents provided. This will instantly direct you to the exact section that contains the information you need most urgently.
Measurement is finding the number which shows the size or amount of something. It can also be described as a technique through which the properties of an object are determined to a standard quantity. It is also referred to as the process or result of determining the magnitude of quantity such as length or mass, relative to a unit of measurement, such as meter or kilogram.
Varieties of Measuring Units.
The units of measurement are the collection of standard and other units that are used to measure various physical quantities. It is a tool to measure and compare different things. Comparison becomes easy when all the units for the measurement are the same.
Contents
Definition of Unit in Maths
Units are the tools to measure and compare different things. Comparison becomes easy when all the units for the measurement are the same. Different units can be classified depending on their use.
A Few of the Units Can be Classified As:
Length: The length evaluates the space or distance between two points or it is the amount of space between two points. For example the distance between the school and house, or the distance from one end of the road to another end.
Below a line having a length AB of 6cm, measured by a ruler is the examples of measurement.

Ruler
The principal unit for measuring length can be described as the following:
Area: Area is the term which is used to describe the amount of space taken up by a 2D shape or surface. The area is measured in square units. The area is calculated by multiplying the length of a shape by its width.

Example of Area
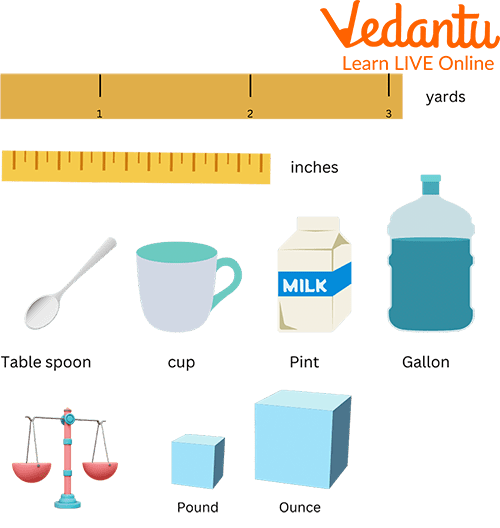
Capacity: Capacity is the maximum amount that something can contain, and volume is the amount of space that a substance or object occupies. The term capacity is used to measure how much fluid fits inside the container. It is measured in milliliters (ml), liters (l), or in imperial, pints and gallons.
1 Liter = 1000 milliliters
1 Kiloliter = 1000 liters

Different Objects Showing the Capacity are the Examples of Measurement
Scales of Measurement
-
Nominal Scale of Measurement: It defines the identity property of data. It contains various characteristics but does not carry any form of numerical meaning. The data can be placed into categories but it cannot be added, subtracted, divided, or multiplied from one another.
-
Ordinal Scale of Measurement: The ordinal scale defines data that is placed in a specific order. These values cannot be added to or subtracted from.
-
Interval Scale of Measurement: It contains properties of nominal and ordered data, but the difference between data points can be quantified. This type of data shows both the order of the variables and the exact differences between the variables. They can be added to or subtracted from each other, but not multiplied or divided.
-
Ratio Scale of Measurement: This includes properties from all the scales of measurement. The data is nominal and defined by an identity, which can be classified in order, contains intervals, and can be broken down into the exact value. Examples of ratio scales are weight, height, and distance. It can be added, subtracted, divided, and multiplied.
Properties of Measurement
-
Identity: It refers to each value that has a unique meaning.
-
Magnitude: It determines whether the object is larger or smaller than other objects of the same kind.
-
Equal Intervals: It means that the differences between numbers (units) anywhere on the scale are the same.
-
A minimum value of zero: It means that the scale has a true zero point.
Solved Examples
Q1. Convert 5km into meters.
Ans: 1km = 1000m
5km = (5 x 1000)m
= 5000m
So 5km in meteres is 5000m.
Q2. Convert 730mm into centimeters.
Ans: 1cm = 10mm
730mm = (730 $div$ 10)cm
= 73cm
Therefore, 730mm into cm is 73.
Q3. How many feet are there in 60 inches?
Ans: 1 feet = 12inches
60inches = (60 $div$12)inches
= 5 feet
So 60 inches in feet is 5 feet.
Practice Questions
Q 1. Convert:
-
35 meters = _____cm
-
20 litres = _____ml
-
12 feet = _____ inches
Ans: 1. 3500 cm
2. 20000 ml
3. 144 inches
Q 2. Add 350kg 20g and 25kg 45 grams.
Ans: 375kg and 65g
Q3. Subtract 200g from 1 kg.
Ans: 800g
Summary
In this article, we learned that measurements play an important role in enhancing the mathematical skills of the students as it is a very basic topic, which is very important to remember as it helps in higher classes. Length, area, and capacity are very basic topics that help in measuring the object very accurately and precisely making it a lot of fun while learning. Depending upon the size of the object it can be measured through different prefixes like liters, kilograms, centimeters, etc.
Thank you so much for taking the time to read the article titled Introduction to the Definition of Measurement in Math written by Math Hello Kitty. Your support means a lot to us! We are glad that you found this article useful. If you have any feedback or thoughts, we would love to hear from you. Don’t forget to leave a comment and review on our website to help introduce it to others. Once again, we sincerely appreciate your support and thank you for being a valued reader!
Source: Math Hello Kitty
Categories: Math