If you happen to be viewing the article Sum of the Measure of the Exterior Angles of the Polygon: An Introduction? on the website Math Hello Kitty, there are a couple of convenient ways for you to navigate through the content. You have the option to simply scroll down and leisurely read each section at your own pace. Alternatively, if you’re in a rush or looking for specific information, you can swiftly click on the table of contents provided. This will instantly direct you to the exact section that contains the information you need most urgently.
A polygon is a two-dimensional shape with a minimum of three sides. The sides may be four, five and so on. The polygon is divided into two parts: regular polygon and irregular polygon. The sum of measures of the exterior angles is the sum of all exterior angles formed in the polygon. In this article, we will learn about exterior angles and the sum of all exterior angles of a polygon.
Contents
- 1 Exterior Angle
- 2 Properties of the Exterior Angles of a Polygon
- 3 Sum of Exterior Angles of a Polygon
- 4 Proof of Sum of the Exterior Angles of the Polygon
- 5 Interior Angles
- 6 Formula for Sum of All Interior Angles of a Polygon
- 7 Proof of the Interior Angles of the Polygon
- 8 Sum of Interior Angles of Different Polygons
Exterior Angle
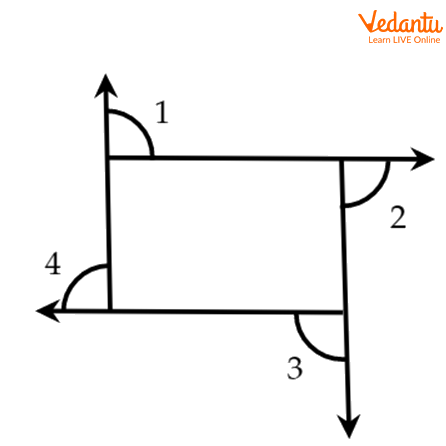
When the side of a polygon is extended, the angle formed outside the figure is called the exterior angle. It is formed between the extended side and the adjacent side.
Four Exterior Angles of a Polygon
Properties of the Exterior Angles of a Polygon
The exterior angle has different properties. Let us consider a hexagon, which is a polygon. Following are the properties, which tell us about the exterior angles:
-
They are formed on the outside of the given figure.
-
The sum of the interior and exterior angles formed by the extended side and the adjacent side is always[180^circ ].
-
In the figure, angles 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6 are the exterior angles.

Hexagon
The exterior angles of a regular polygon are always equal to each other.
Sum of Exterior Angles of a Polygon
As we have taken the hexagon here, we start from the first vertex and proceed in the clockwise direction. The bending happens at the different vertices 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6 and ends at vertex 1. In this way, we covered a full rotation and this complete angular rotation is [360^circ ]. Therefore, it concludes that the sum of exterior angles of a polygon is [360^circ ].

Exterior Angle
Proof of Sum of the Exterior Angles of the Polygon
Let us consider the polygon is a convex polygon with n number of sides and N is the sum of its exterior angles.
By the exterior angle theorem,
The sum of exterior angles is equivalent to the sum of interior angles and the sum of linear pairs.
[;{rm{N}} = {rm{ }}180n – 180 times left( {{rm{n}} – 2} right)]
Now, we will perform the calculations step by step.
[{rm{N}} = 180n – 180{rm{n}} + 360^circ ]
[{rm{N}} = ,,360^circ ] [;]
In this way, we proved that the sum of the exterior angles of the polygon is[360^circ ].
Interior Angles
Interior angles of any two-dimensional shape are the measure of the angles between its sides within the closed figure. These are the inclinations of one side to another side. A polygon has three sides, i.e., a triangle, which will have three interior angles. If the polygon were a quadrilateral, the figure would have four interior angles.

Interior Angle
Formula for Sum of All Interior Angles of a Polygon
The sum of all interior angles of a polygon is equal to the[left( {{rm{n}} – 2} right), times ,180^circ ]. Here, n is some sides of the polygon. The polygon here may be a triangle, quadrilateral, pentagon, hexagon etc.
Proof of the Interior Angles of the Polygon
We know that the sum of interior angles of a polygon having [n]sides is[left( {{rm{n}} – 2} right), times ,180^circ ].
Consider a polygon of sides ABCDE; it is divided into 3 triangles by joining the diagonals such that the figure is divided into subsequent triangles. There is a polygon having n sides.

ABCDE is a Polygon Divided into Three Triangles
It is clear that when the polygon has n sides, it forms [left( {{rm{n}} – 2} right)] triangles.
By angle sum property, the sum of all angles triangle=[180^circ ].
The sum of the angles of[({rm{n}} – 2)] triangles = [left( {{rm{n}} – 2} right), times ,180^circ ]
In this way, the value of each interior angle of a regular polygon is
=[][dfrac{{({rm{n}} – 2) times 180^circ }}{{rm{n}}}]
Sum of Interior Angles of Different Polygons
Interesting Facts
-
The smallest polygon is a triangle and the largest polygon we study is a decagon. The largest is other, but we do not study that in our curriculum.
-
The sum of the interior and its corresponding exterior angle will always[180^circ ].
-
Polygons can have more than 12 sides. It can be any number more than 3. The polygon having 99 sides is called enneacontagon.
Solved Problems
1. If there are seven numbers of sides in a regular polygon, find the measure of each exterior angle.
Ans: Since the sum of all exterior angles of a polygon[ = ;360^circ ]
The measure of each angle [, = ,dfrac{{360^circ }}{{rm{n}}}]
[ = dfrac{{360}}{7}]
[ = 51.42^circ ]
2. There are eight sides in an irregular polygon. What is the sum of all interior angles? What is the name of the polygon?
Ans: The polygon has sides. Therefore, the polygon here is an octagon.
Sum of all interior angles [ = left( {{rm{n}} – 2} right), times ,180^circ ]
[begin{array}{l};;;;;;;;;;;;;;;; = {rm{ }}left( {8 – 2} right) times 180^circ \;end{array}]
[ = 1080^circ ]
3. If there is a sum of all the interior angles of a regular polygon is[540^circ ]. Calculate the number of sides.
Ans: Sum of all interior angles [ = left( {{rm{n}} – 2} right), times ,180^circ ]
[540^circ ; = left( {{rm{n}} – 2} right), times ,180^circ ]
[;;dfrac{{540^circ }}{{180^circ }};, = {rm{n}} – 2]
[3 = {rm{n}} – 2]
[{rm{n}},, = ,,3 + 2]
[{rm{n}} = 5]
Key Features
-
In the above study, we studied the following key features:
-
Sum of all the exterior angles of any type of polygon is[360^circ ].
-
Sum of all interior angles of any type of polygon is [(n-2)times,180^{circ} ]..
-
The value of each exterior angle of a regular polygon is [,dfrac{{360^circ }}{{rm{n}}}].
-
In an irregular polygon, the measure of each adjacent interior angle is subtracted [180^circ ].
-
The value of each interior angle of the polygon is calculated by [dfrac{{({rm{n}} – 2) times 180^circ }}{{rm{n}}}]
Practice Questions
1. If the sum of interior angles is[1080^circ ], then what is the name of this polygon? How many sides are there (n=8, octagon)?
2. If the ratio between an exterior and interior angle of a polygon is 1:5. Find the value of each exterior and interior angle ([30^circ ,150^circ ]).
3. Is it possible that a polygon has an external angle[45^circ ]? Give proper reasons. (Yes)
Thank you so much for taking the time to read the article titled Sum of the Measure of the Exterior Angles of the Polygon: An Introduction written by Math Hello Kitty. Your support means a lot to us! We are glad that you found this article useful. If you have any feedback or thoughts, we would love to hear from you. Don’t forget to leave a comment and review on our website to help introduce it to others. Once again, we sincerely appreciate your support and thank you for being a valued reader!
Source: Math Hello Kitty
Categories: Math